Is Type 2 Diabetes Serious? Causes, Symptoms, Risk and Tests

On this page
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease that results in your body's inability to control blood sugar properly. In a healthy body, Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, assists your cells in taking in glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream for energy consumption. In the case of type 2 diabetes, your body either resists insulin (insulin resistance) or does not produce enough insulin.
The above-mentioned type 2 diabetes symptoms lead to high blood sugar levels, which in turn leads to multiple other health issue if left untreated.
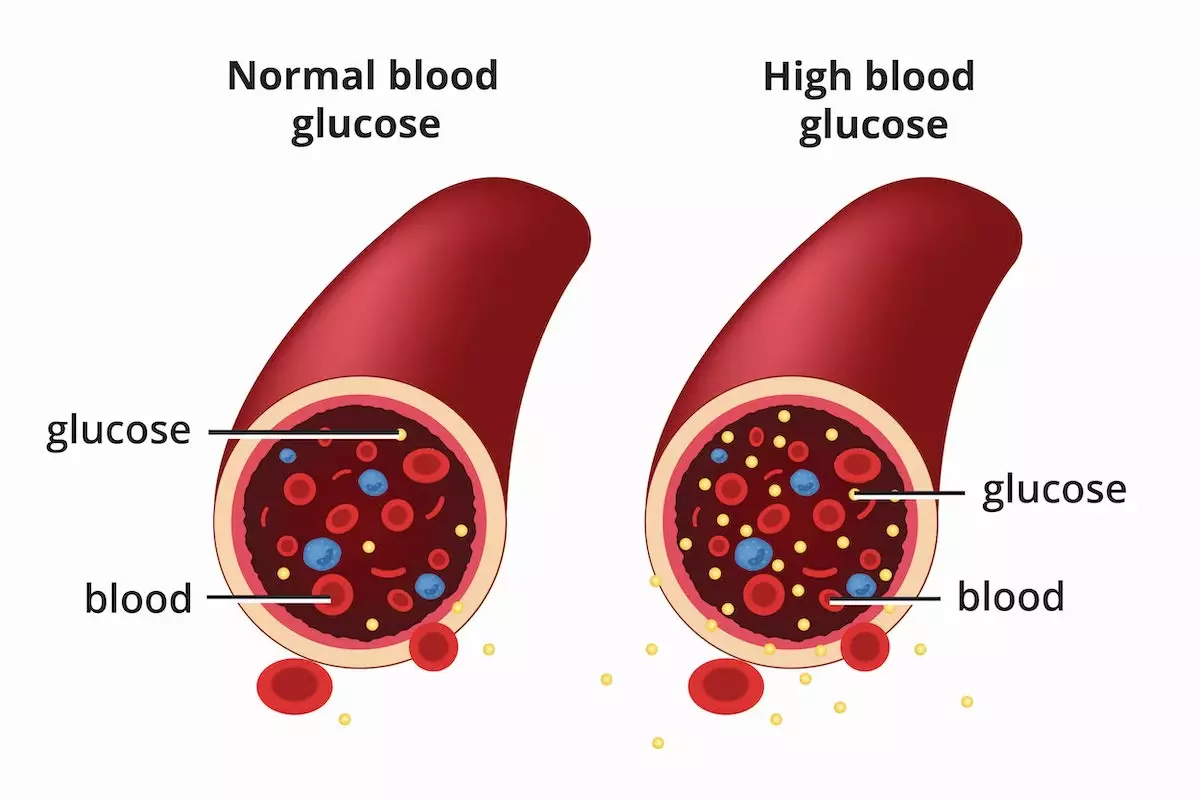
Overview: Type 2 Diabetes
The most prevalent type of diabetes is type 2 diabetes, which accounts for nearly 90% of all diabetes cases. It is usually a long-term illness and can sometimes remain undetected for years. On the positive side of the story, with the proper test for diabetes and by controlling it through diet, exercise and medication if necessary, you can have a normal life and control your diabetes.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes causes are multifactional inheritance and thus multiple factors involved in pathogenosis
-
Genetics: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes raises your possibility. If one parent bears type 2 diabetes, your risk is raised by 2 to 4 times compared to the person without a family history of this condition. If you have both parents with type 2 diabetes, your risk goes up dramatically.
-
Overweight and obesity: Too much weight, especially visceral fat, can be a risk factor for insulin resistance. The fat cells may prevent the action of insulin making it more difficult for the body to utilise glucose correctly.
-
Physical inactivity: Consistent physical activity enhances the insulin sensitivity. During the exercise, your muscles grab glucose from the blood for the energy, and this causes the blood sugar levels to go down.
-
Unhealthy diet: Overeating processed foods, sugary drinks, and bad fats is also associated with an increased Risk. These foods can increase blood sugar levels and cause weight gain, two risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
8 Warning Signs of Type 2 Diabetes
The signs of type 2 diabetes are often subtle and progressive over time. Here are eight warning signs to be aware of:
-
Increased thirst and frequent urination: When your blood sugar is increased, your kidneys work harder to get rid of the extra sugar from your blood, causing you to pee more often (polyuria). You will also get the urge to drink water more often if you experience polydipsia.
-
Excessive hunger: Even though you are probably consuming more, the cells are not able to get the glucose they need because of insulin resistance. It can therefore cause an increased appetite also known as polyphagia.
-
Unexplained weight loss: Weight loss could be a good thing, but not if it happened unintentionally. At times, weight loss with type 2 diabetes happens when your body is tearing down muscle for energy, as it can’t access glucose effectively.
-
Fatigue and low energy: The blood circulating in your body for a long time with a high level of sugar may interfere with the body’s ability to use energy efficiently, resulting in fatigue and tiredness.
-
Blurred vision: High blood sugar level for a long time can harm the eyes' blood vessels, resulting in blurry visions. This is because fluid fills the vessels into the area of the eye responsible for sharp vision (macula).
-
Slow-healing sores: Diabetes often hurts circulation and delays the healing process of wounds, cuts, and injuries. In fact, high blood sugar levels can directly damage the nerves and the blood vessels of the affected area, thereby limiting the flow of blood to it.
-
Frequent infections: High blood sugar can create an immunocompromised situation, giving rise to ectopic yeast infections and skin infections. This could happen because white blood cells that fight infection can not function properly in a high blood sugar condition.
-
Areas of darkened skin: The darkened areas in the armpits and groyne are associated with insulin resistance, a feature of type 2 diabetes. This is referred to as acanthosis nigricans, which may arise due to insulin increase that drives the skin cells to grow.
It should be stressed that not all type 2 diabetes patients will experience all these signs and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. Should you have multiple type 2 diabetes symptoms, you need to see your doctor to get a proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis for Type 2 Diabetes
The test for type 2 diabetes includes a variety of tests. These include:
-
A fasting blood sugar test: A regular fasting blood sugar test for diabetes measures your blood sugar after at least 8 hours of no food intake, usually overnight. If you have a fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or more on two tests, it is likely to be diabetes type 2.
-
Postprandial blood sugar Test: Sugar level is measured 1 hour after a meal.
-
An HbA1c test: This blood test is used to determine your average blood sugar level over the course of the past two-three months. An A1C level of 6.5% or more on two consecutive times indicates type 2 diabetes. We use HPLC Method which provide the most accurate level of HbA1c to evaluate glycemic control in past 3 month.
-
An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): This type 2 diabetes test involves drinking a sugary beverage and blood sugar levels being measured at intervals. An OGTT is used less often than the A1C test or fasting blood sugar test for type 2 diabetes diagnosis but it may be used when results of the other tests are not quite clear.
-
C-peptide level
-
Insulin level
-
S fructosamine: In the same case where HbA1c can not be used for glycemic control evolution s fructosamine is done in those patients for glycemic control evaluation.
Early identification of type 2 diabetes is essential for preventing adverse effects of the disease. Does your doctor tell you that you have any concerns or the risk factors of type 2 diabetes? If yes, then it is important to ask your doctor about the test for type 2 diabetes.
Who Is at Risk for Type 2 Diabetes?
You can get type two diabetes even if you don't have a prior family history of the disease, but certain risk factors may be more important than others. Here's who might be at higher risk:
-
Those having a family history of type 2 diabetes
-
Those who are above the standard weight or obesity
-
Those who are not accustomed to physical activities
-
Women who also have gestational diabetes
-
People with prediabetes (having blood sugar levels higher than normal, but not yet at a level to qualify for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis)
-
There are people who have a PCOS background
-
Some ethnic groups (like Hispanic/Latino, African American, Asian American and Native American)
If you have type 2 diabetes you should work closely with your doctor to control your blood sugar levels and prevent subsequent health problems
Author Bio:
City X-Ray's team of healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing clear, informative content on type 2 diabetes, empowering you to take control of your health.
DISCLAIMER: THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE. The information including text, graphics, images, and other material contained on this website is for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Contact a health expert if you have questions about your health.












Comments List