Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis
On this page
Overview
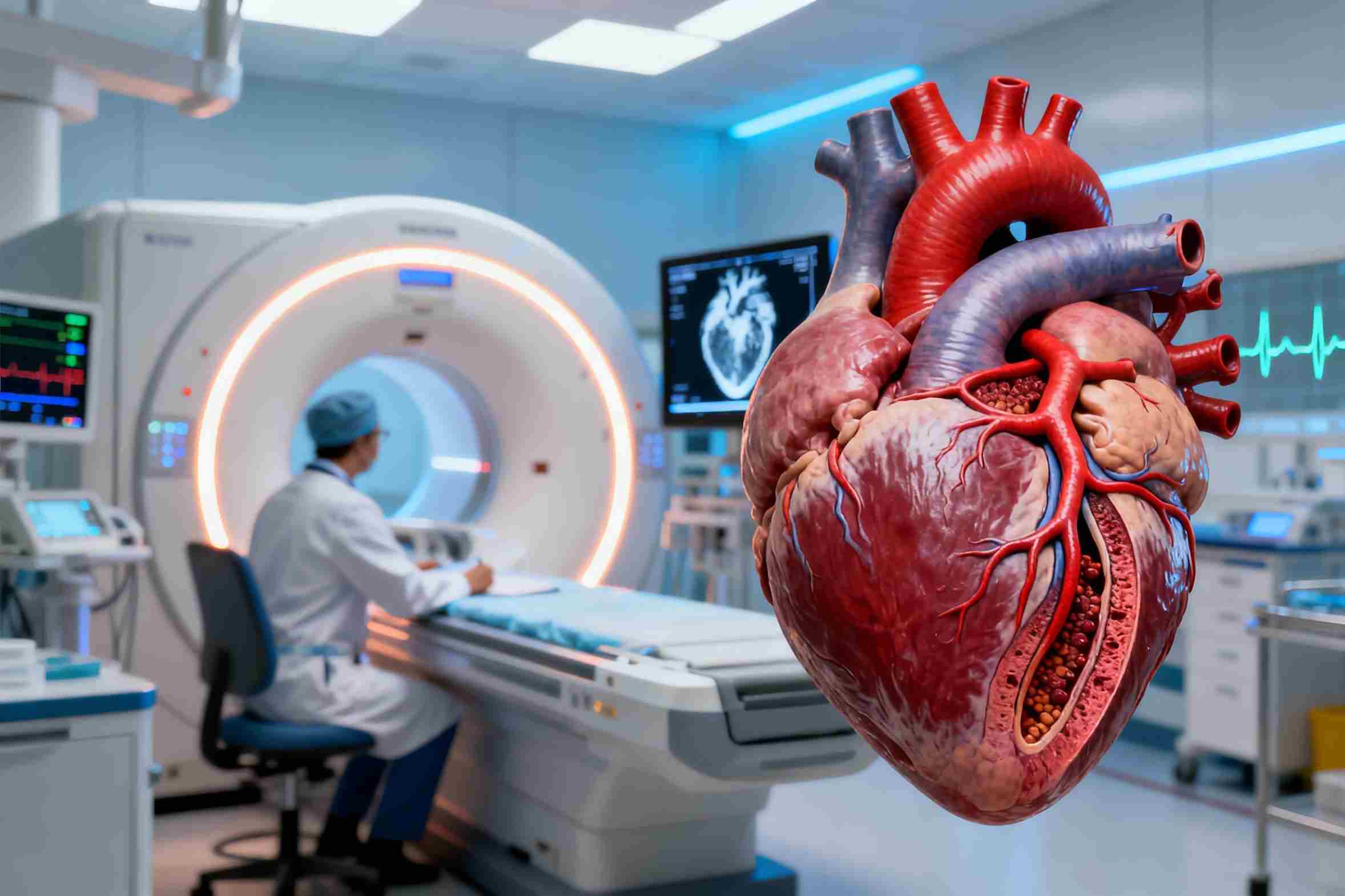
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) occurs when the coronary arteries — the vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart — become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup over time. This plaque is made of cholesterol, calcium, fats and other materials. As the arteries narrow, less blood reaches the heart muscle. In some cases, the plaque can suddenly rupture and form a clot, completely blocking blood flow and causing a heart attack.
CAD often develops silently for many years. Many people do not feel symptoms until a blockage becomes severe — which is why CAD is commonly known as a “silent killer.”
What Causes CAD?
The main cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a gradual hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque accumulation. Several factors increase your chances of developing coronary artery disease:
-
High blood pressure
-
Smoking or tobacco use
-
Obesity or high BMI
-
Lack of exercise
-
Unhealthy diet rich in saturated fats and refined carbs
-
Family history of heart disease
-
Older age
-
Stress and poor sleep
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Many people have no symptoms for years. When symptoms do appear, they usually include:
-
Chest pain or pressure (angina) — often triggered by physical activity or emotional stress
-
Shortness of breath, even with mild activity
-
Fatigue or reduced exercise capacity
-
Heart attack, which may be the first noticeable sign
Complications of CAD
If left untreated, CAD can lead to:
-
Heart attack
-
Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
-
Heart failure
-
Sudden cardiac arrest
Early detection prevents most of these complications.
Diagnosis: How CAD Is Detected
Doctors diagnose coronary artery disease through a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests and advanced imaging.
Common diagnostic steps include:
-
Blood pressure check
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
-
Review of your symptoms and risk factors
Imaging Tests for CAD
Modern imaging helps identify plaque buildup and blockages before they become dangerous. At City X Ray, you can access advanced cardiac imaging such as:
CT Coronary Angiography (CT-CTA)
A highly detailed, non-invasive scan that shows:
-
Narrowing of coronary arteries
-
Plaque buildup
-
Calcium deposits
-
Early signs of heart disease
CT- CTA is often recommended as one of the first imaging tests for patients with chest pain or suspected CAD. It is quick, safe and provides clear 3D images of your coronary arteries.
Coronary Calcium Score
Measures calcium buildup in coronary arteries to assess long-term heart disease risk.
City X Ray provides both tests with expert reporting and cardiologist-ready results.
Treatment & Management
Treatment depends on severity but generally includes:
-
Heart-healthy diet
-
Regular exercise
-
Quitting smoking
-
Medications to lower cholesterol, blood pressure or prevent clots
-
In some cases, stents or bypass surgery may be needed
Imaging plays a key role in deciding which treatment approach is best.
Prevention
While genetics and age cannot be changed, many risk factors for CAD can be controlled:
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Eat a balanced, low-fat diet
-
Stay physically active
-
Manage diabetes and blood pressure
-
Avoid smoking
-
Reduce stress
-
Monitor cholesterol regularly
If you have family history or multiple risk factors, early screening is highly recommended.
When to Seek Medical Help
Consult your doctor or visit an imaging center if you experience:
-
New or worsening chest discomfort
-
Shortness of breath
-
Unexplained fatigue
-
Family history of heart disease
-
High cholesterol, diabetes or hypertension
Emergency care is needed if symptoms resemble a heart attack.
How City X Ray Helps
City X Ray & Clinical Labs provides reliable diagnostic support for heart disease through:
-
Advanced CT Coronary Angiography
-
Coronary calcium scoring
-
Lipid profile and cardiac blood tests
-
Fast reporting and cardiology referral support
Our goal is early detection — so treatment can be started before complications develop.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the early warning signs of Coronary Artery Disease?
Early symptoms are often subtle and include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and reduced exercise tolerance. Many people may have no symptoms until the disease becomes severe, which is why early screening is important.
2. How is CAD diagnosed, and which imaging test is best?
Diagnosis involves ECG, lipid profile, stress tests, and advanced imaging. CT Coronary Angiography (CT-CTA) is the most detailed, non-invasive test to detect blockages early. Coronary Calcium Score helps assess long-term risk.
3. Can Coronary Artery Disease be reversed?
CAD cannot be fully reversed, but progression can be slowed or stabilized with lifestyle changes, weight management, exercise, medication, and quitting smoking. Early detection gives the best chance to prevent complications.
4. What is the difference between CT Coronary Angiography and a Calcium Score test?
-
CT-CTA: Shows blockages, plaque buildup, and artery narrowing in real time.
-
Calcium Score: Measures calcium only; indicates long-term risk but doesn’t show active blockages.
Doctors often use both for better risk assessment.
5. When should someone consider getting a CT Coronary Angiography?
You should consider CT-CTA if you have chest pain, breathlessness, family history of heart disease, high cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, or multiple cardiac risk factors. It is also recommended for individuals above 40 with lifestyle-related risks.












.webp)


Comments List