Fatigue: Symptoms, Reasons, Tests and Prevention Tips

On this page
Overview
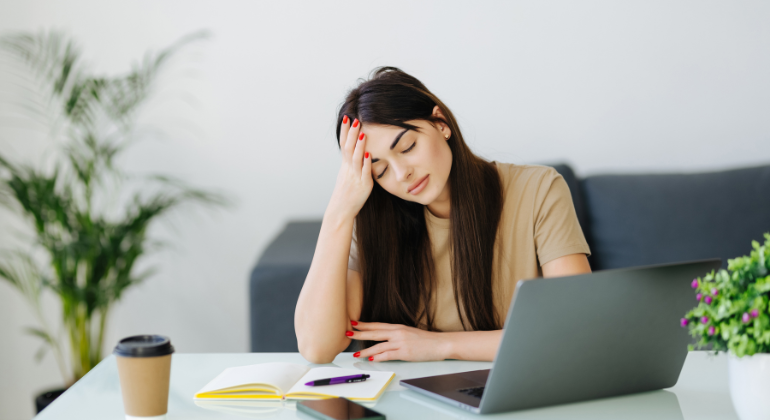
Fatigue is a condition far deeper than simple tiredness. It is a continuous feeling of exhaustion that affects your body, mind, and productivity. Today, people of all ages suffer from chronic fatigue due to lifestyle habits, stress, hormonal changes, sleep disorders, and underlying health issues. Many individuals ignore this tiredness, assuming it is normal — but persistent fatigue can be an early sign of medical conditions that require proper attention.
This detailed guide explains what fatigue feels like, why it is more common in women, what symptoms to look out for, which tests are essential, how to prevent fatigue, and why a trusted diagnostic centre like City X-Ray & Scan Clinic is ideal for complete evaluation.
What is Fatigue?
Fatigue is a condition where your body feels drained of energy even after resting. Unlike simple tiredness, fatigue lasts for days, weeks, or even months. It affects your ability to work, think, focus, and enjoy daily life. People experiencing fatigue may feel:
- Constant exhaustion
- Mental dullness
- Body heaviness
- Slow reactions
- Irritation or mood swings
Common Fatigue Symptoms
Fatigue shows up in many forms. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent tiredness
- Muscle aches or heaviness
- Difficulty concentrating (brain fog)
- Short-term memory issues
- Slow decision-making
- Irritability or mood imbalance
- Lack of motivation
- Sleepiness even during the day
- Feeling out of breath
- Headaches
- Low stamina
- Feeling mentally overwhelmed
If these symptoms continue for more than two weeks, you should consider a health evaluation.
Female Fatigue: Why Women Experience More Fatigue
Fatigue is widespread among females due to biological, lifestyle, and emotional responsibilities. Women often balance multiple roles — household duties, office work, childcare, and emotional labour, all of which create continuous mental and physical strain.
Main reasons for fatigue in females include:
Iron Deficiency (Anaemia)
Most women lose blood during their monthly periods. Heavy bleeding reduces haemoglobin levels, causing severe weakness and breathlessness.
Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism is more common in women, causing fatigue, weight gain, hair loss, and slow metabolism.
Hormonal Imbalance
PMS, PCOS, pregnancy, post-delivery changes, breastfeeding, and menopause all impact energy and mood.
Emotional Load
Women naturally take on emotional responsibilities — caring for parents, partner, children — leading to mental fatigue.
Sleep Disturbance
Stress, hormonal fluctuation, childcare responsibilities, or anxiety disturb sleep, reducing energy.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Low levels of B12, Vitamin D, magnesium, and folate often cause chronic fatigue.
Chronic Health Conditions
PCOS, fibromyalgia, autoimmune disorders, depression, and anxiety can create long-term fatigue.
Other General Causes of Fatigue
Fatigue in men and children can also be caused by:
- Poor sleep quality
- Stress, anxiety, overthinking
- Excessive workload
- Poor nutrition
- Obesity or a sedentary lifestyle
- Diabetes
- High or low blood pressure
- Heart issues
- Kidney or liver diseases
- Medications
- Chronic infections
- Lack of hydration
Fatigue can also happen after viral infections or long-term illness.
When Fatigue Should Not Be Ignored
Some fatigue symptoms indicate a serious medical condition:
- Fatigue lasting more than 2–3 weeks
- Sudden weakness or dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Pale skin
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Severe mood changes
- Persistent headaches
Tests for Fatigue — Main Diagnostic Tests Doctors Recommend
When fatigue lasts for weeks or affects daily life, doctors recommend specific investigations to identify underlying causes.
Here Are the Main Tests for Fatigue:
- CBC Blood Test (Complete Blood Count)
- Thyroid Function Tests (TSH, T3, T4)
- Vitamin Tests – Vitamin B12 & Vitamin D
- Iron Studies / Ferritin Test
- Blood Sugar Test (Fasting, PP, HbA1c)
- Kidney Function Test (KFT Blood Test)
- Liver Function Test (LFT)
- Electrolyte Test (Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium)
- Hormone Tests (for Females: LH, FSH, Prolactin, Estrogen, Testosterone)
- ECG or Stress Test
- Sleep Study (Polysomnography)
How to Prevent Fatigue — Practical Tips
You can reduce fatigue with the following healthy habits:
- Maintain consistent sleep routine
- Eat a protein-rich, iron-rich, vitamin-rich diet
- Drink plenty of water daily
- Exercise regularly (walking, stretching, yoga)
- Manage stress
- Take small breaks during long work hours
- Avoid heavy meals late at night
- Reduce caffeine, alcohol, and smoking
- Spend time in sunlight for Vitamin D
- Don’t skip meals
Why Choose City X-Ray & Scan Clinic for Fatigue Evaluation?
City X-Ray & Scan Clinic is a trusted choice for fatigue-related testing because:
- Experienced doctors & advanced laboratory setup
- Accurate and fast reports
- Affordable test packages
- Home sample collection available
- Doctor-reviewed reports and proper guidance
Conclusion
Fatigue is not just tiredness — it is your body’s alarm. Whether physical, mental, or hormonal, fatigue affects your health, productivity, mood, and overall well-being. Instead of ignoring persistent fatigue, get accurate testing to find the root cause.
With complete diagnostic services and expert evaluation, City X-Ray helps you understand your body better and regain your lost energy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the most common fatigue symptoms?
Common fatigue symptoms include constant tiredness, weakness, low stamina, difficulty concentrating, and daytime sleepiness. Some people may also experience muscle aches, mood swings, and reduced motivation. If these symptoms continue for more than two weeks, it’s important to get a medical evaluation to find the underlying cause.
2. Why do females experience more fatigue?
Women often experience more fatigue because of hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Iron deficiency, thyroid problems, stress, lack of sleep, and managing multiple responsibilities also contribute. These factors drain both physical and mental energy, making fatigue more common and intense in females.
3. Can dehydration cause fatigue?
Yes. Dehydration reduces blood volume, slows oxygen supply, and affects muscle and brain function. This leads to tiredness, headaches, dizziness, and low energy. Drinking enough water throughout the day and maintaining proper hydration can significantly reduce fatigue caused by dehydration.
4. When should I get tested for fatigue?
If fatigue persists for more than 2–3 weeks, affects your daily routine, or is accompanied by symptoms like dizziness, mood changes, shortness of breath, or irregular periods, you should get tested. Persistent fatigue often indicates underlying issues like anemia, thyroid imbalance, vitamin deficiency, or chronic illness.
5. Can fatigue be treated?
Yes. Fatigue improves once the underlying cause is identified and treated. Conditions like anemia, thyroid imbalance, vitamin deficiency, or hormonal problems respond well to medical treatment. Along with proper medication, good sleep, a balanced diet, hydration, and stress management help restore energy levels.
6. What are signs of chronic fatigue syndrome?
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome involves extreme tiredness lasting longer than six months. Symptoms include unrefreshing sleep, memory problems, muscle pain, headaches, dizziness, and worsening fatigue after physical or mental activity. It significantly affects daily life and requires proper diagnosis to manage symptoms effectively.






.webp)

.webp)



Comments List